
Sciencedoze is a free learning platform where you can explore blogs of Science, Education and Technology. You can follow us on Facebook to be a member of this community.
A ceramic is an inorganic, non-metallic solid mainly based on oxide, nitride, boride, or carbide that are shaped and then fixed at high temperatures. Ceramic is hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant.

Ceramic is used almost everywhere like in kitchens, cookware, pottery, bricks, pipes, etc.
Many ceramics contain a mixture of ionic and covalent bonds between them. That's why they exist in crystalline, semi-crystalline, and vitreous form.
1. Ceramics have high hardness.
2. They are brittle and have poor toughness.
3. They have a high melting point.
4. They have poor electrical and thermal conductivity.
5. They have low ductility.
6. They have a high modulus of elasticity.
7. They have high compression strength.
8. They show optical transparency to a variety of wavelengths.
1. Silicon carbide and tungsten carbide are technical ceramics that are used in body armor, wear plates for mining, and machine components due to their high abrasion resistance.
2. Uranium oxide (UO2) is a ceramic that is used as a nuclear reactor fuel.
3. Zirconia is a ceramic that is used to make ceramic knife blades, gems, fuel cells, and oxygen sensors.
4. Barium titanate is a ceramic that is used to make heating elements, capacitors, transducers, and data storage elements.
5. Stealite is a ceramic that is used as an electrical insulator.
Oxide ceramics contains oxide fibers which include a combination of Zirconium dioxide, aluminum trioxide, and titanium dioxide. The oxide fibers help ceramics to withstand oxidation and provide strength and reinforcement.
Following are some types of oxide ceramics:
Alumina ceramics have high chemical resistance, increased strength, and high-temperature resistance. Alumina ceramics can be manufactured from its powder form then corresponding it and then fired overheat.

The final product is rough which can be smoothened using silica coating which further enhances its strength.
Beryllium oxide ceramics have good thermal conductivity, high insulation, low dielectric constant, low medium loss, and good process adaptability.
Beryllium oxide ceramics are used as a component in glass and that glass is used to make X-ray tubes which are used for medical purposes.
Beryllium oxide ceramics are also used for high-power microwave packaging and high-frequency transistor packaging due to their good stability and insulation properties.
Zirconia ceramics are less brittle than other ceramics and have low thermal conductivity, excellent thermal insulation, and very high resistance to crack propagation. They are used for protective coatings, dental services, and making ceramic knives.
Non-oxide ceramics offer a great replacement to oxide ceramics because oxide ceramics can't be used in extreme environments and can't bear heavy loads.
Non-oxide overcomes all these limitations of oxide ceramics because they have high corrosion resistance, hardness, and oxidation resistance. They even don't degrade till 2400 C temperature.
Following are the two most common types of non-oxide ceramics:
Silicon nitride ceramics have low density, high fracture toughness, good flexural strength, and excellent thermal shock resistance.
Silicon nitride ceramics are used for rotating bearing balls and rollers, cutting tools, moving engine parts, turbine blades, and weld positioners.
Silicon carbide ceramics are much lighter and harder than other ceramics and are resistant to acid. They have a low thermal expansion, high conductivity, and are chemically stable.
![]()
They are used for making fixed are moving turbine components, suction box covers, seals, bearing, ball valve parts, and heat exchangers.
Composite ceramics is made up of two or more constituent materials with different physical or chemicals properties.
These materials combine to produce a material having different properties than individual components. Composite ceramics have ceramics fibers embedded in the ceramic.
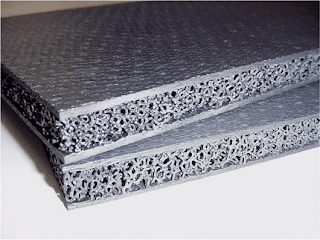
Fiber-reinforced ceramics is also known as ceramic matrix-fiber composite. It has increased toughness, high strength, and polycrystalline structure.
Due to their ability to resist high temperature and resistance, they are used in heat shield systems like burners, flame holders, and hot gas ducts.
Classification of ceramics can be given on how they are used:
Structure ceramics are clay-based (generally) which are pressed into shape according to our need. They have good insulating properties which can be altered by changing their density. The denser the ceramic, the lower the insulating properties.
Structural ceramics includes bricks, dinner bricks, dinner plates, and statues.
Ceramics that can hold their shape and strength at high temperatures are called refractory ceramics. That's why they are used in furnaces and kilns. They are made using oxide like silicon dioxide, titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, and many other oxides.
Electrical ceramics or electroceramics are known for their excellent electrical properties. They have good mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties which make them versatile for use. The conductivity of electrical ceramics increases when the temperature increases.
For example Dielectric ceramics, fast ion conductor ceramics, etc.
Magnetic ceramics are oxide materials that show a certain type of permanent magnification (ferrimagnetism).
Magnetic ceramics are made up of ferrites which are crystalline minerals composed of iron oxide combine with some other metal. Magnetic ceramics are used in a variety of places like in transformer, telecommunication, and information recording.
Abrasives ceramics can be natural or synthetic which are used to grind or cut away other softer material. They have high hardness, wear-resistance, and high toughness.
For example, Diamond, Silicon carbide (SiC), tungsten carbide (WC), etc.
What is a Crime Scene ? A place where the crime is committed or where the maximum physical evidence related to crime is found is known as a crime scene. A crime scene is a starting point of the investigation which provides information about the suspect and the victim. This helps to reconstruct the crime and fast resolution of the case. It is noted that the crime scene is not limited to a single place but may extend to a wider area depending upon the nature of the crime committed. For example, In a murder case where murder is done at one place and the body is disposed on another place. In this case, we have two crime scenes that give information about the crime. Types of Crime Scene Based on evidence found on the crime scene: 1. Primary Crime Scene The crime scene where the actual crime occurred or where more usable pieces of evidence were found is known as the primary crime scene. For example, A murder scene, theft, assault, etc. 2. Secondary Crime Scene The crime scene which is some

What are Conducting Polymers? As the name suggests organic polymers that conduct electricity are known as conducting polymers. They are also known as intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) and they have alternating single and double bonds along the polymer backbone (conjugated bonds) or that are composed of aromatic rings such as Phenylene, naphthalene, anthracene, pyrrole, and thiophene which are connected through carbon-carbon single bonds. Examples: Polyacetylene, Polypyrrole, Polyaniline, etc What is the reason behind conducting nature of these polymers? Conducting polymers comes in two forms that are doped conducting polymers and non-doped conducting polymers. The conductivity of non-doped conjugated polymers is due to the existence of a conductivity band similar to a metal. In a conjugated polymer, three of the four valence electrons form strong sigma bonds through sp² hybridization where electrons are strongly localized. The remaining unpaired electron of each carbon atom re

What is documentation of the crime scene and Why it is done? After securing the crime scene, the next most important step is documentation of the crime scene because documentation permanently records the crime scene and its physical evidence. Documentation should be done without any wastage of time as the scene and its evidence may get altered over time. The documentation should be done innovatively and the originality of the crime scene should be maintained and documentation should not have pauses or breaks, it should remain constant till the whole crime scene is documented. There are four main tasks of documentation that is note-making, photography, videography , and sketching . It should be noted that all four tasks are necessary and none is a substitute for another. For example, notes are not substitutes for photography, video is not a substitute for sketching, etc. Following are the sequence for crime scene documentation: 1. Note making Documentation of crime scene in the f